The second Trump administration has ushered in a significant shift in U.S. foreign policy, particularly in its approach to Russia. By deprioritizing full support for Ukraine and seeking a diplomatic resolution with Moscow, Trump’s administration appears to be engaging in a strategic realignment that many critics view as appeasement. The core rationale behind this policy shift is Washington’s increasing preoccupation with China. Rather than confronting Russia as a long-term adversary, Trump’s team is recalibrating U.S. priorities, aiming to prevent a Sino-Russian alliance that could pose a formidable challenge to American global dominance.
This policy has sparked intense debate. Supporters argue that Washington’s resources should be concentrated on countering Beijing’s economic and military rise, rather than entangling the U.S. in a prolonged and costly European conflict. They contend that reaching an understanding with Moscow—potentially including the lifting of sanctions, halting Ukraine’s NATO ambitions, and reopening diplomatic channels—could deter Russia from deepening its ties with China and create a more manageable geopolitical environment. However, opponents warn that such an approach risks repeating the historical mistakes of appeasement. They argue that giving concessions to Moscow without securing firm commitments emboldens Russian President Vladimir Putin, weakens NATO’s credibility, and undermines the U.S.’s long-standing commitment to European security.
This analysis will examine Trump’s Russia policy through a multidimensional lens, assessing its geopolitical, military, economic, and domestic political ramifications. By evaluating the potential benefits and pitfalls, this commentary will argue that while the strategy may offer short-term diplomatic flexibility, its long-term consequences could ultimately weaken American influence, fracture transatlantic alliances, and embolden revisionist powers.
The Strategic Rationale Behind Trump’s Russia Policy
At the heart of Trump’s Russia policy is a fundamental reassessment of U.S. strategic priorities. Unlike previous administrations that sought to contain both Russia and China, Trump’s team operates on the premise that China represents the primary existential threat to U.S. global leadership. This worldview has led to a recalibration of Washington’s approach to Moscow, where confrontation with Russia is seen as a distraction rather than a necessity.
The Primacy of China in U.S. Grand Strategy
Trump’s foreign policy has long been shaped by a zero-sum approach to great-power competition, in which U.S. resources must be concentrated on the most pressing adversary—China. In contrast to the Cold War, when the Soviet Union was seen as America’s primary rival, today’s strategic landscape is defined by China’s rapid economic rise, technological advancement, and military expansion in the Indo-Pacific.
Several key factors drive this perception:
- Economic Competition: China has overtaken the U.S. as the world’s largest trading nation and continues to challenge American dominance in sectors like artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and critical supply chains.
- Military Modernization: The People’s Liberation Army (PLA) is expanding its blue-water navy, hypersonic weapons capabilities, and regional military bases, threatening U.S. dominance in the Indo-Pacific.
- Geopolitical Ambitions: Beijing’s assertiveness in the South China Sea, Taiwan Strait, and Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) signals a long-term challenge to U.S. influence, particularly in Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
For Trump, Russia is no longer the primary threat but a secondary actor whose geopolitical aspirations, though problematic, do not pose an immediate challenge to U.S. supremacy. The administration’s goal is not to align with Russia but to prevent it from fully aligning with China.
The Nixon Playbook: Reversing the Cold War Strategy
Trump’s strategic approach mirrors President Richard Nixon’s 1972 opening to China, in which Washington sought to exploit Sino-Soviet divisions by engaging Beijing to contain Moscow. Today, Trump appears to be flipping that approach—seeking détente with Russia to isolate China.
The logic behind this shift is straightforward:
- China and Russia together form a potent geopolitical bloc that can challenge U.S. hegemony. Their growing economic and military cooperation—exemplified by joint military exercises, energy deals, and diplomatic alignment in forums like BRICS—poses a strategic dilemma for Washington.
- By engaging Russia, Trump seeks to drive a wedge between Moscow and Beijing, ensuring that Russia does not fully support China in a potential U.S.-China confrontation, particularly over Taiwan.
- The U.S. does not need Russia as an ally, but it cannot afford to let Russia become China’s junior partner in a prolonged geopolitical struggle.
A Transactional Approach to Foreign Policy
Trump’s foreign policy is defined by a transactional mindset, where diplomatic engagement is viewed through the lens of short-term gains rather than ideological commitments. Unlike previous administrations that framed foreign policy in terms of democratic values, alliances, and long-term strategy, Trump prioritizes deal-making and immediate cost-benefit calculations.
Under this framework, Russia is seen as a potential negotiating partner rather than an ideological adversary. Trump’s outreach to Moscow is therefore part of a broader attempt to reshape U.S. global priorities in a way that maximizes short-term flexibility while focusing on long-term competition with China.
The Risks of Miscalculation
While the strategic logic behind Trump’s Russia policy is clear, it carries significant risks. The most immediate concern is that Russia may exploit U.S. concessions without fundamentally altering its geopolitical trajectory. Unlike during the Cold War, when Nixon successfully leveraged China against the Soviet Union, today’s Russia-China partnership is far more stable and mutually beneficial.
Key risks include:
- Russia’s Long-Term Ties with China: Despite U.S. overtures, Russia has little incentive to distance itself from China, given their shared anti-Western rhetoric, economic interdependence, and strategic alignment.
- Encouraging Russian Aggression: By downplaying NATO’s importance and engaging with Russia diplomatically, Trump risks emboldening Putin, who may interpret U.S. concessions as a green light for further territorial expansion in Ukraine or even beyond.
- Fracturing U.S. Alliances: Trump’s retreat from traditional European commitments could push allies to seek alternative security arrangements, weakening the transatlantic relationship that has underpinned Western stability since World War II.
In the next section, we will analyze how this policy translates into concrete actions, including military, diplomatic, and economic measures, and assess its broader implications for global stability.
The Policy in Practice: Concessions to Russia and Their Consequences
Trump’s strategic recalibration of U.S.-Russia relations has translated into tangible policy decisions that reflect a shift from confrontation to engagement. These moves, whether through military posturing, diplomatic negotiations, or economic decisions, have significant implications for European security, NATO cohesion, and the broader global order.
Military and Security Concessions: Weakening NATO’s Eastern Flank
One of the most contentious aspects of Trump’s Russia policy has been his ambiguous commitment to NATO. While previous U.S. administrations reinforced NATO’s presence in Eastern Europe as a deterrent against Russian aggression, Trump’s approach signals a retreat from traditional security commitments.
Key actions include:
- Downplaying Article 5 Obligations: Trump has repeatedly suggested that NATO members should shoulder a greater share of their defense burden, raising concerns that the U.S. may not come to the defense of Eastern European allies in the event of Russian aggression.
- Shifting the Burden to Europe: Trump’s administration has called on European NATO members to increase their defense spending to at least 5% of GDP, a move that reflects a desire to offload security responsibilities onto allies rather than maintain a strong U.S. military presence in Europe.
- Ending Lethal Aid to Ukraine: One of the most direct policy shifts has been the curtailment of U.S. military aid to Ukraine, which had been a cornerstone of Western efforts to resist Russian advances. Trump’s decision to halt further military assistance effectively weakens Ukraine’s ability to defend itself.
Consequences:
- Increased Russian Military Adventurism: With the U.S. signaling a reduced commitment to NATO, Russia may see an opportunity to test Western resolve by escalating hybrid warfare tactics or cyber operations in Eastern Europe.
- Weakened NATO Deterrence: If the U.S. is perceived as an unreliable security partner, European nations may pursue independent defense strategies, weakening the cohesion of NATO.
- Encouragement of Strategic Ambiguity: Russia has historically exploited Western indecision and divisions, and Trump’s policies risk creating the very uncertainty that emboldens Russian expansionism.
Diplomatic Realignments: Direct U.S.-Russia Negotiations
Trump’s administration has prioritized direct diplomacy with Moscow, often at the expense of traditional multilateral frameworks involving European allies and Ukraine. This approach mirrors his bilateral negotiation style, where personal diplomacy is emphasized over institutional agreements.
Key moves include:
- Sidestepping Ukraine and European Allies: The S.-Russia talks in Riyadh, which marked the first high-level diplomatic engagement between the two countries since 2022, notably excluded Ukraine and key European nations from the negotiations. Ukrainian President Zelenskyy openly criticized the move, arguing that it undermines Ukraine’s sovereignty and territorial integrity.
- Trump-Putin Phone Calls and Private Diplomacy: Trump has repeatedly praised Putin in public statements, while engaging in direct, unscripted calls with the Russian president. Reports indicate that these conversations often involve strategic discussions that bypass traditional diplomatic channels.
- Encouraging Peace Talks on Russian Terms: The administration has signaled that a ceasefire in Ukraine should be negotiated with Russian demands in mind, effectively pressuring Ukraine to accept territorial concessions as part of any settlement.
Consequences
- Sidelining European Security Interests: The exclusion of European powers from negotiations weakens EU diplomatic leverage and could push countries like France and Germany to pursue independent security policies outside of U.S. leadership.
- Legitimizing Russian Expansionism: By engaging Moscow without preconditions, Trump risks normalizing Russia’s territorial gains, undermining the principle of national sovereignty.
- Damaging Transatlantic Trust: The move has already shaken confidence in U.S. leadership, with European officials openly questioning America’s commitment to NATO and European security.
Economic Engagement: Sanctions Relief and Energy Policy Shifts
Trump’s administration has also signaled a shift in economic policy toward Russia, favoring selective sanctions relief and potential trade engagement to encourage Moscow to distance itself from Beijing.
Key economic measures include:
- Easing Sanctions on Russia: Reports indicate that the administration is considering lifting key economic sanctions imposed on Russia since 2014, particularly those affecting the energy and financial sectors.
- Potential U.S.-Russia Business Deals: Some senior Trump administration officials have floated the idea of allowing S. companies to re-enter Russian markets, particularly in the energy and natural resources sectors. Russian officials have already suggested that American corporations could regain access to lucrative Russian investments if relations improve.
- Blocking Further European Energy Sanctions: Trump has discouraged additional European restrictions on Russian energy imports, arguing that sanctions hurt Western economies more than they weaken Moscow.
Consequences
- Strengthening Russia’s Economy: Sanctions relief would provide a much-needed economic boost to Russia, allowing Putin to sustain his military efforts and solidify domestic control.
- Undermining Western Sanctions Unity: If the U.S. weakens sanctions, Europe may struggle to maintain economic pressure on Russia, leading to fragmentation in the Western approach.
- Deepening Russian Leverage in Energy Markets: Trump’s reluctance to impose stricter energy sanctions could increase European dependence on Russian energy, limiting NATO’s strategic options.
Policy Alternatives and Conclusion
Trump’s Russia policy is based on the idea that Moscow can be encouraged to move away from Beijing in return for U.S. diplomatic and economic incentives. However, as outlined in the previous sections, this strategy carries significant risks, particularly in terms of weakening NATO, emboldening Russian aggression, and diminishing U.S. global credibility. Instead of concessions without conditions, the U.S. could pursue alternative approaches that balance strategic pragmatism with deterrence.
Policy Alternatives: A Balanced Approach
Rather than outright appeasement, the U.S. should adopt a dual-track approach toward Russia—one that engages Moscow where necessary but maintains deterrence where critical. The following policy recommendations outline a more balanced alternative to Trump’s strategy.
Conditional Diplomatic Engagement
Instead of unconditional bilateral negotiations with Russia, U.S. diplomatic outreach should be contingent on Moscow’s behavior.
Direct engagement with Russia should only proceed if Moscow demonstrates concrete de-escalation measures in Ukraine—such as withdrawing from occupied territories or committing to ceasefire agreements.
Multilateral diplomacy must remain the core approach—any negotiations should involve Ukraine and key European allies to avoid undermining transatlantic security.
Maintaining NATO Deterrence While Sharing the Burden
While European nations should increase their defense spending, the U.S. must reaffirm its NATO commitments, particularly on the eastern flank, where Russian threats remain high.
The U.S. should expand joint military exercises in Eastern Europe, reinforcing deterrence while ensuring that Europe takes on a greater role in its own defense.
Instead of reducing U.S. military aid to Ukraine, Washington should provide security assistance in ways that empower Ukraine’s self-defense capabilities, rather than forcing Kyiv into a settlement on Russia’s terms.
Sanctions as a Bargaining Tool, Not a Giveaway
Economic sanctions should not be lifted without reciprocal actions from Russia. Instead of offering concessions upfront, the U.S. should use sanctions as a bargaining tool to extract verifiable commitments from Moscow.
The U.S. should coordinate with European allies to maintain a unified sanctions regime, preventing economic fragmentation that could weaken the West’s leverage.
Keeping Russia from Becoming Overly Dependent on China
Limited economic engagement with Russia could be selectively explored, particularly in areas where the U.S. can provide alternatives to Chinese influence.
The U.S. could engage in economic diplomacy with countries like India and Türkiye, which maintain ties with Russia, to create economic incentives for Moscow to diversify beyond China.
Cooperation on non-military global issues—such as nuclear arms control and Arctic governance—could be areas where Washington and Moscow maintain dialogue without undermining Western security interests.
The Bigger Picture: Why Trump’s Russia Policy is a Strategic Miscalculation
While Trump’s policy seeks to reduce tensions with Russia to focus on China, the approach is deeply flawed for three reasons:
- Russia Will Not Abandon China: The assumption that Moscow will distance itself from Beijing in exchange for U.S. goodwill is unrealistic. Russia and China’s strategic partnership is driven by shared anti-Western interests, making it unlikely that Russia would align with Washington against China.
- Appeasement Undermines U.S. and Allied Security: Historical precedent shows that concessions without enforcement invite further aggression—whether it was Neville Chamberlain’s appeasement of Nazi Germany or Western inaction toward Russia’s annexation of Crimea in 2014. By weakening U.S. deterrence in Europe, Trump’s strategy could embolden not just Russia, but also China and other revisionist powers, increasing the likelihood of conflicts in multiple regions.
- The U.S. Cannot Afford to Weaken NATO While Confronting China: The Indo-Pacific strategy against China depends on strong transatlantic alliances. Weakening NATO undermines U.S. credibility globally, making it harder to build coalitions in Asia. If European allies lose trust in the U.S., they may hedge their security with alternative arrangements, reducing Washington’s ability to project power globally.
Conclusion: A Strategic, Not Transactional, U.S. Foreign Policy
Trump’s Russia policy represents a significant departure from traditional U.S. strategy, prioritizing a narrow focus on China over the broader implications of global security. While engagement with Russia is not inherently flawed, the unconditional concessions granted to Moscow risk undermining U.S. credibility, weakening NATO, and emboldening authoritarian aggression.
A more effective alternative approach would involve selective engagement with Moscow while maintaining military deterrence, strengthening NATO, and using economic leverage strategically. Rather than gambling on Russia’s willingness to break from China, the U.S. must pursue a comprehensive strategy that preserves Western security while countering the long-term challenge posed by both China and Russia.
If the lesson of history is clear, it is that appeasement rarely secures peace—instead, it invites further destabilization. The challenge for U.S. policymakers will be ensuring that any engagement with Moscow strengthens, rather than undermines, global stability.
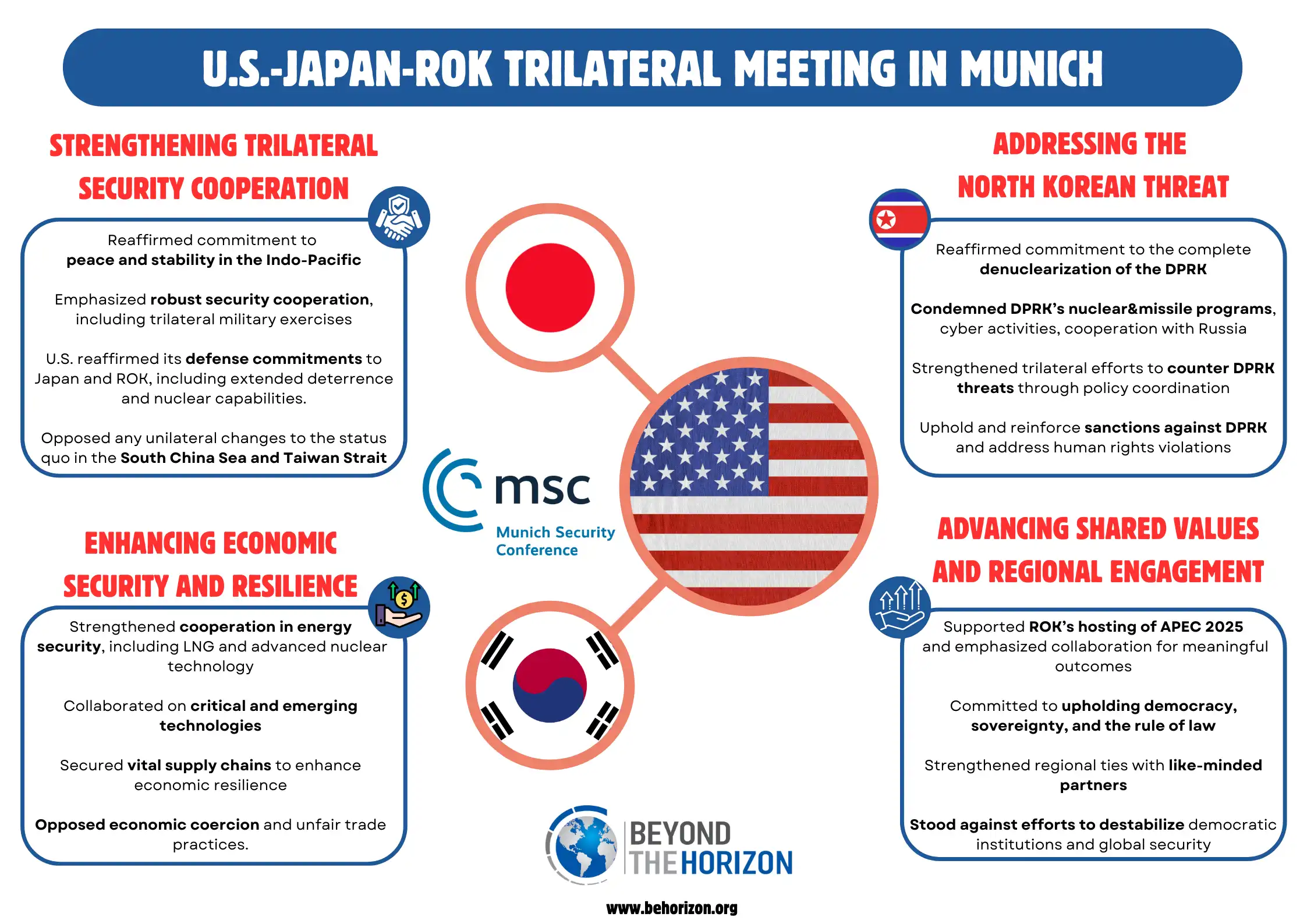
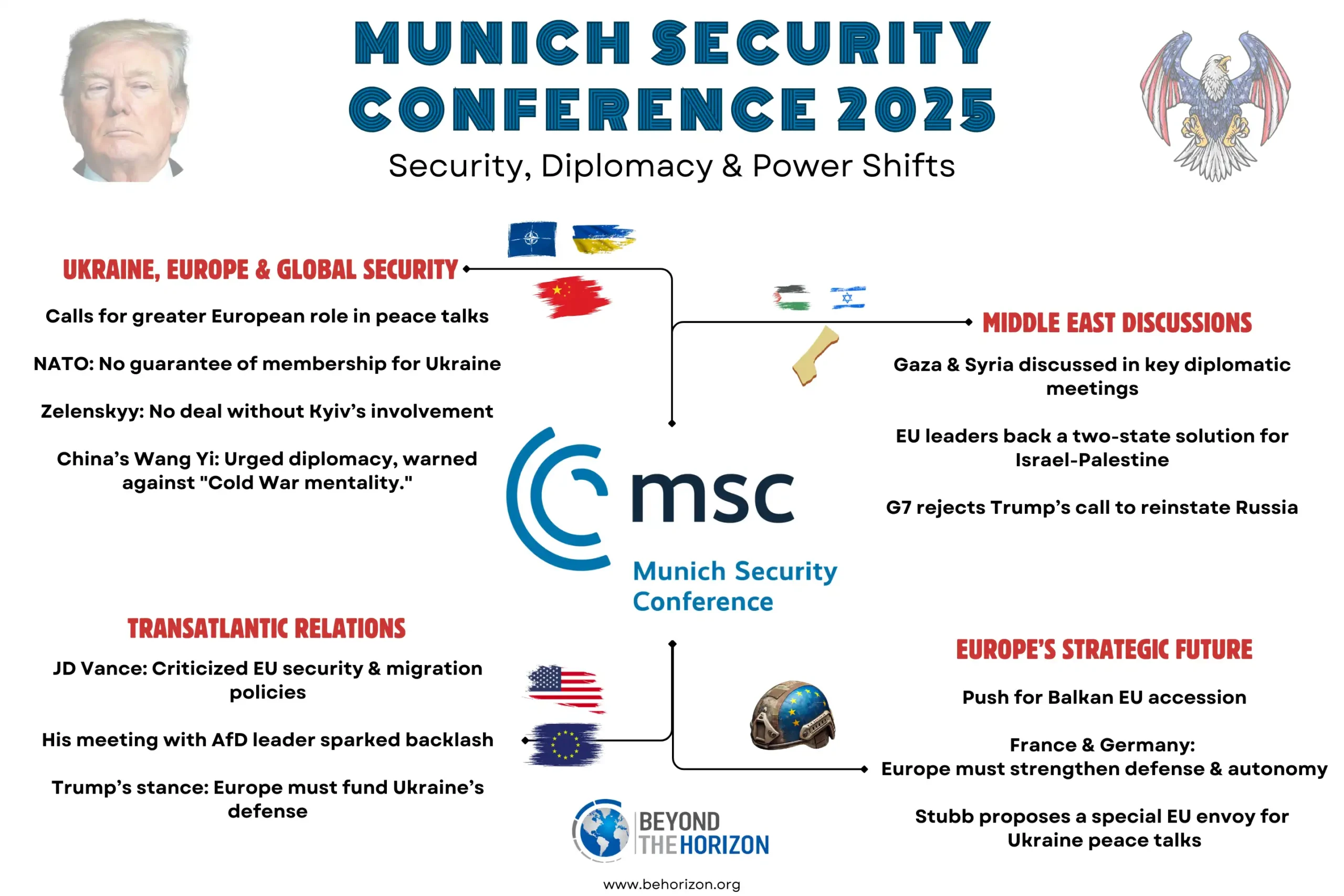
Related Infographics