Summary
- JCPOA is very crucial to stability in the Middle East, and to prevent nuclear proliferation in the region.
- This time, the US could not unilaterally exert influence upon its European Allies and the Security Council. The Europeans dismissed the idea that the US imposition of sanctions can trigger a snapback since the US withdrew the agreement. Thus, this is a (temporary) success of the EU and other countries against the “maximum pressure” policy of the US.
- Saving JCPOA will prove the actorness of the Union and its credibility.
- Global politics is becoming more dangerous at the age of great power politics along with furious US president pursuing a harsh unilateralism and maximum pressure strategy. There is a need for pushback to keep the multilateralism alive.
The UN arms embargo against Iran was expired on 18 October 2020 despite the objection and complaint of the US. E3 (Germany, France , and the UK), China, and Russia dismissed the idea that the US imposition of sanctions should trigger the snapback mechanism because the US had already withdrawn the agreement. This time the US failed to unilaterally exert influence on either its European Allies or on China and Russia. Therefore, the expiration may provide some fresh air to the deal that has been in the emergency room due to the US withdrawal and sanctions crippling Iran’s economy. The expiration does not affect the sanctions imposed by the US; however, it represents a symbolic victory for Iran.
The US position vis-à-vis JCPOA is dependent upon the results of the incoming US elections since former Vice-President promised to return the deal. However, we should take into account that JCPOA is a product of European Foreign Policy in E3 format with the support of the Obama administration. In case Joe Biden takes office, the old spirit may be revived; however, if Donald Trump is reelected, then the survival of the Iranian Nuclear Deal is solely reliant on the efforts of the EU. In both cases, the EU has a prominent role in JCPOA
The Iranian Nuclear Deal is an important issue for international security and also for the stability in the Middle east. Moreover, JCPOA is an experiment for the EU to prove its global actorness as the guardian of multilateralism against President Trump, who acts unilaterally and believes `maximum pressure` policy.
EU Commission Von Der Leyen labelled the EU as the ‘guardian of multilateralism’ during the presentation of her team. The Union attaches the utmost significance to multilateralism and rule-based world order. European Security Strategy, the first strategy of the Union, stated that the EU wants to strengthen international organizations and regimes to confronting threats through ‘effective multilateralism’. European Global Strategy, published in 2016, employs ‘multilateral’ or ‘multilateralism’ 16 times.
Starting after the invasion of Iraq, the EU has disagreed with the US over the methods to resolve Iran’s nuclear dossier and preferred a neoliberal approach through soft power and effective multilateralism. The EU was the pioneer of the agreement with its diplomatic approach. The Union used its ability of soft power, i.e. ‘change preferences of countries by attraction rather than coercion’. The EU took the lead and generated a framework that serves the interest of everyone with compromises by pursuing multilateral diplomacy over different channels, e.g. E3, European Union, UNSC. Hence, JCPOA can be seen as a salient manifestation and achievement of this strategy.
The EU brought parts to the table and found common ground not only between the US and Iran, but also China and Russia. It created a win-win deal for everyone on a sensitive dossier like nuclear energy via multilateralism instead of conflicts or regime change. Furthermore, the nuclear issues are part of the Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) regime, the only international authority to say something about it is the UNSC. Thus, the deal is signed by P5+1, i.e. UN Security Council plus Germany, meaning that it cannot be overridden by another country or any other organization. The agreement is also incorporated into the UNSC Resolution 2231 and became a binding as a part of international law.
JCPOA created a unique institutionalized mechanism for Iran’s nuclear program. For the first time in history, Iran is the first country that has accepted this amount of restraints and inspections by its own will. Some of the restrictions in JCPOA is as follows:
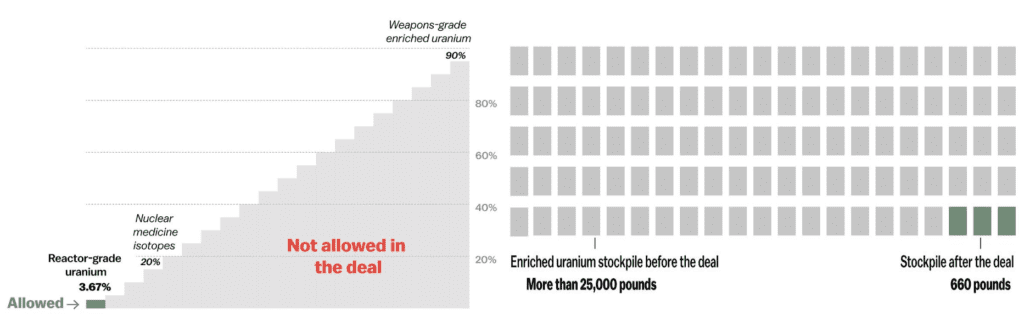
- Iran would decrease the enrichment below 3.67 % (dropped from 25,000 to 660 pounds)
- Iran would not employ more than 5,060 centrifuges (dropped from 20,000)
- Iran would not operate any facility other than the one at Natanz.
- Iran’s breakout time is increased from 2 months to one year.
- Independent inspectors from IAEA will check the compliance.
- In case of a non-compliance, there will a snapback of sanctions
- The sanctions and restrictions on Iran will be lifted.
Source: Vox
The deal decreased Iranian nuclear activity to an acceptable extent, in turn, the sanctions will be revoked, and the pressure from the international community would be diminished. Frozen assets can be used, and Iran would be gradually integrated into the international market. Over time, the relations may normalize, and Iran is exposed to the West gradually instead of China and Russia.
Exposure generates interdependencies and socialization, which enable the EU and the West to transform Iran very slowly but steadily instead of regime change. Iran can spend less on military and more for its public in terms of wealth, culture, health care, and so forth. Even if this fails, it can create diplomatic channels, and overcome the problems through diplomacy and multilateralism.
One of the biggest challenges the Union faced was the need to convince the US, especially for the compliance of Iran. The US avers that Iran tries to develop its nuclear capacity covertly while agreeing on the deal to achieve a certain extent of relief by avoiding sanctions. However, JCPOA has got ‘the most robust verification mechanisms’ in the world, as the IEAE director points it out. Moreover, the deal includes a Dispute Resolution Mechanism -triggered in 2020 by E3- has a provision of snapback against non-compliance.
JCPOA has far-reaching implications for the stability in the Middle East. As Iran gradually decouples from its nuclear program, security dilemmas with other countries such as Saudi Arabia, Turkey, Egypt, and even Israel can be overcome. In an optimistic scenario, this can lead to a Nuclear-free zone in the region in the future. After isolating nuclear issues, problems in the region can be handled more easily through diplomacy.
There are challenges in front of European diplomacy and its adherence to multilateralism. The most prominent one is the first risk in ‘Top Risks 2020’ published by Eurasian Group: President Trump. He withdrew from the deal in 2018, started to implement a ‘maximum pressure’ policy, and there is maximum pushback from Iran. From this point, we will see an increasing weaponized interdependence in global politics by the US. Consequently, maintaining JCPOA via multilateralism will be a daunting task for the European Union.
Recommendations
- The EU must employ all assets at its disposal for recovering the deal, particularly its Market Power even if the Union has to pushback against the US.
- The EU has to strengthen INSTEX mechanism to encourage European companies against the US sanctions. As of now, INSTEX is not seen as a viable alternative to the SWIFT system.
*Research fellow at Beyond the Horizon ISSG

